********** UNIVERSITY **********
return to top
From UCLA to Columbia, Professors Nationwide Defend Students as Politicians and Police Attack
Thu, 02 May 2024 21:15:55 +0000
University faculty have put their bodies and livelihoods on the line amid a brutal, violent response to student protests for Gaza.
The post From UCLA to Columbia, Professors Nationwide Defend Students as Politicians and Police Attack appeared first on The Intercept.
On campus, inside the Capitol, and in court, there’s an all-out assault on American democracy in the name of Israel.
The post They Used to Say Arabs Can’t Have Democracy Because It’d Be Bad for Israel. Now the U.S. Can’t Have It Either. appeared first on The Intercept.
The movement to divest from Israel and the defense industry is gaining momentum on college campuses.
The post “A New Sense of World-Building”: Inside the Student Movement for Gaza appeared first on The Intercept.
The last big protests cost $150 million in NYPD overtime — with tens of millions more in lawsuit settlements.
The post How Much Money Did the NYPD Waste Quashing Student Protests? We Tallied It Up. appeared first on The Intercept.
Two college protesters were placed in solitary confinement, according to Columbia professors who worked in real time to support jailed students.
The post After Raids, NYPD Denied Student Protesters Water and Food in Jail appeared first on The Intercept.
The bipartisan duo also praised schools that brought in police to violently quell protests and connected the demonstrations to the TikTok ban.
The post In No Labels Call, Josh Gottheimer, Mike Lawler, and University Trustees Agree: FBI Should Investigate Campus Protests appeared first on The Intercept.
Nahla Al-Arian lost more than 200 relatives in Israel's attacks on Gaza. Then Eric Adams said she was the reason police raided Columbia.
The post NYC Mayor Smeared a Grandmother as an “Outside Agitator” to Justify NYPD Assault on Columbia appeared first on The Intercept.
When police attacked student protesters, a lone trash can was the only damaged property I saw around City College of New York.
The post I’ve Covered Violent Crackdowns on Protests for 15 Years. This Police Overreaction Was Unhinged. appeared first on The Intercept.
The famed scholar on why reducing Hamas to a terrorist label sanctions Israel’s war on Palestinians.
The post Judith Butler Will Not Co-Sign Israel’s Alibi for Genocide appeared first on The Intercept.
The cookbook author scores, salts and stuffs the eggplants with a cheesy and herby breadcrumb mix. The result? A soft and saucy vegetarian midweeker
Eggplant is the introverted extrovert of the vegetable kingdom: slow to warm up, sure, but before long it’s the life of the party. Like any I-E, this nightshade needs time and tools to break down its defences, lest it be served up in its naturally bitter, astringent form; if you’ve ever bitten into an eggplant and it bit back, that’s because it’s undercooked.
No one likes to risk bitey eggplant, which is why – despite its marvellous meatiness – many home cooks shy away from it as a meat-free midweeker. But by halving, slashing and then salting it you also halve its cooking time.
Continue reading...Bernard and Ann McDonagh admit five joint charges of fraud after not paying at four restaurants and one takeaway
A couple from south Wales have admitted carrying out a string of “dine and dash” offences, racking up large bills for food and drink before leaving without paying.
Bernard McDonagh, 41, and Ann McDonagh, 39, from Port Talbot, admitted five joint charges of fraud and will be sentenced at Swansea crown court this month.
Continue reading...James Watt steered the brewer to great success but a private equity stake and attending Nigel Farage’s 60th suggest the edginess is gone
The extraordinary success of the Scottish beer and bars company BrewDog owes much to a shrewd realisation on the part of its co-founder, James Watt.
The 42-year-old, who announced his departure as chief executive on Wednesday, realised early on that punk, once a subculture, could be turned into a lucrative marketing brand.
Continue reading...“The reality for kids living there is shocking, honestly,” said an official who recently returned from Gaza. “People are living in really squalid conditions.”
The post 600,000 Palestinian Kids in Rafah Can’t “Evacuate” Safely, UNICEF Official Says appeared first on The Intercept.
The bakery that gave the world the £25 croissant has gone one better. But is the giant new pastry made to be eaten – or posed with?
Name: The £28 pain au chocolat.
Age: Fresh out of the oven.
Continue reading...Click here to submit a picture for publication in these online galleries and/or on the Guardian letters page
Continue reading...The climate crisis is making the farming business unsustainable – and without support for us, food security will suffer too
Farming has always been a risky business. To the chaos of Brexit and the relentless squeezing of the supermarkets, we can add the rapidly escalating threats associated with climate change. In most industries, at the point where risk is judged to outweigh the potential commercial reward, both capital and people tend to make a swift exit, following economist Adam Smith’s “invisible hand” of self-interest.
The problem with farming is that most farmers are emotionally invested in their work. An exit is seldom considered – perhaps we should be more like the bankers, but they wouldn’t be much good at growing potatoes.
Continue reading...Climate chaos is threatening food production, trade and lives, says World Meteorological Organization
Hunger and disease are rising in Latin America after a year of record heat, floods and drought, a report by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) has shown.
The continent, which is trapped between the freakishly hot Pacific and Atlantic Oceans, probably suffered tens of thousands of climate-related deaths in 2023, at least $21bn (£17bn) of economic damage and “the greatest calorific loss” of any region, the study found.
Continue reading...Baked cheesecake, American-style, is a classic for good reason
Cheesecake, which in reality is more a tart than a cake, comes in many forms, from the creamy, set fruit-topped numbers in the freezer section of the supermarket to the magnificently charred Basque variety that the Observer’s Jay Rayner complained was “bloody everywhere” last year. This is a simpler baked version, based on a classic American recipe and perfect for pairing with seasonal fruit.
Prep 25 min
Cook 1 hr 50 min
Makes 1 cake, about 20cm
Devastating floods in Rio Grande do Sul state have about left 90 dead with survivors seeking food and shelter
Heavy rains that began last week have caused rivers to flood, inundating whole towns and destroying roads and bridges across the southern Brazilian state of Rio Grande do Sul.
The local civil defence agency said the death toll had risen to 90, while 131 people were unaccounted for with 155,000 homeless. A state of emergency has been declared in 397 of Rio Grande do Sul’s 497 towns and cities as rescue efforts continue.
The Taquari River in Rio Grande do Sul. Photographs: Maxar Technologies/AFP/Getty Images
Continue reading...He tackled a murderer to the ground to protect the public. But the draconian licence conditions of his ‘99-year sentence’ meant that the first person he called was his probation officer
Marc Conway was regarded as a model IPP prisoner. Perhaps the model IPP prisoner. He received an indeterminate imprisonment for public protection (IPP) sentence at 30 for armed robbery. Before that, he had committed a long list of crimes including driving without a licence, selling class A drugs and firearm offences. He had spent eight years in jail. Now, here he was, a free man, studying with students from the University of Cambridge, working for the Prison Reform Trust and delivering speeches to the great and the good.
The date was 29 November 2019. The occasion was the fifth-anniversary celebration of an educational project in which Cambridge students and prisoners learned together. Conway, who had taken part in the project, had been asked to give a speech at Fishmongers’ Hall, a Grade II* listed building in the City of London. “It was a lovely sunny day. You never get that weather in November in London,” he says. “We had food, we was laughing, we was joking, we was patting each other on the back. I was getting a bit nervous, because I’d only been out a year and I was still new to public speaking.”
Continue reading...With the world’s humanitarian system in crisis, many NGOs now recognise that local charities can deliver much more at far less cost
Before civil war engulfed her Ethiopian home region of Tigray in 2020, Tsega Girma was a prosperous trader who sold stationery and other goods. But when hungry children displaced by the conflict started appearing in the streets, she sold everything and used the proceeds to buy them food.
After that money dried up, Tsega appealed to Tigray’s diaspora for donations. At the height of the war, her Emahoy Tsega Girma Charity Foundation provided meals to 24,000 children a day.
Continue reading...Two college protesters were placed in solitary confinement, according to Columbia professors who worked in real time to support jailed students.
The post After Raids, NYPD Denied Student Protesters Water and Food in Jail appeared first on The Intercept.
When police attacked student protesters, a lone trash can was the only damaged property I saw around City College of New York.
The post I’ve Covered Violent Crackdowns on Protests for 15 Years. This Police Overreaction Was Unhinged. appeared first on The Intercept.
A weekly email from Yotam Ottolenghi, Meera Sodha, Felicity Cloake and Rachel Roddy, featuring the latest recipes and seasonal eating ideas
Each week we’ll send you an exclusive newsletter from our star food writers. We’ll also send you the latest recipes from Yotam Ottolenghi, Nigel Slater, Meera Sodha and all our star cooks, stand-out food features and seasonal eating inspiration, plus restaurant reviews from Grace Dent and Jay Rayner.
Sign up below to start receiving the best of our culinary journalism in one mouth-watering weekly email.
Continue reading...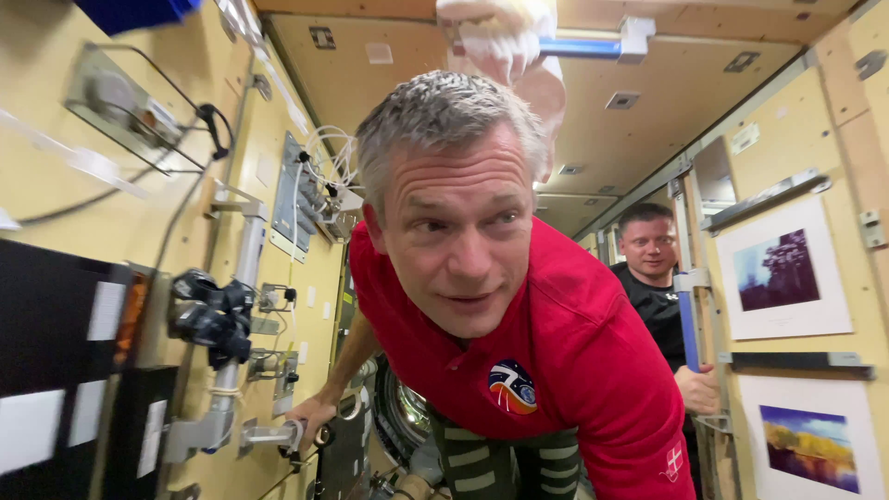 Video:
00:07:30
Video:
00:07:30
On the last day of his Huginn mission, ESA astronaut Andreas Mogensen takes us on a tour of the place he called home for 6 months: the International Space Station. From the beautiful views of Cupola to the kitchen in Node 1 filled with food and friends and all the way to the science of Columbus, the Space Station is the work and living place for astronauts as they help push science forward.
Style, with substance: what’s really trending this week, a roundup of the best fashion journalism and your wardrobe dilemmas solved, direct to your inbox every Thursday
Style, with substance: what’s really trending this week, a roundup of the best fashion journalism and your wardrobe dilemmas solved, delivered straight to your inbox every Thursday
Explore all our newsletters: whether you love film, football, fashion or food, we’ve got something for you
Continue reading... |
Imagine a world in which you can do transactions and many other things without having to give your personal information. A world in which you don’t need to rely on banks or governments anymore. Sounds amazing, right? That’s exactly what blockchain technology allows us to do.
It’s like your computer’s hard drive. blockchain is a technology that lets you store data in digital blocks, which are connected together like links in a chain.
Blockchain technology was originally invented in 1991 by two mathematicians, Stuart Haber and W. Scot Stornetta. They first proposed the system to ensure that timestamps could not be tampered with.
A few years later, in 1998, software developer Nick Szabo proposed using a similar kind of technology to secure a digital payments system he called “Bit Gold.” However, this innovation was not adopted until Satoshi Nakamoto claimed to have invented the first Blockchain and Bitcoin.
A blockchain is a distributed database shared between the nodes of a computer network. It saves information in digital format. Many people first heard of blockchain technology when they started to look up information about bitcoin.
Blockchain is used in cryptocurrency systems to ensure secure, decentralized records of transactions.
Blockchain allowed people to guarantee the fidelity and security of a record of data without the need for a third party to ensure accuracy.
To understand how a blockchain works, Consider these basic steps:
Let’s get to know more about the blockchain.
Blockchain records digital information and distributes it across the network without changing it. The information is distributed among many users and stored in an immutable, permanent ledger that can't be changed or destroyed. That's why blockchain is also called "Distributed Ledger Technology" or DLT.
Here’s how it works:
And that’s the beauty of it! The process may seem complicated, but it’s done in minutes with modern technology. And because technology is advancing rapidly, I expect things to move even more quickly than ever.
Even though blockchain is integral to cryptocurrency, it has other applications. For example, blockchain can be used for storing reliable data about transactions. Many people confuse blockchain with cryptocurrencies like bitcoin and ethereum.
Blockchain already being adopted by some big-name companies, such as Walmart, AIG, Siemens, Pfizer, and Unilever. For example, IBM's Food Trust uses blockchain to track food's journey before reaching its final destination.
Although some of you may consider this practice excessive, food suppliers and manufacturers adhere to the policy of tracing their products because bacteria such as E. coli and Salmonella have been found in packaged foods. In addition, there have been isolated cases where dangerous allergens such as peanuts have accidentally been introduced into certain products.
Tracing and identifying the sources of an outbreak is a challenging task that can take months or years. Thanks to the Blockchain, however, companies now know exactly where their food has been—so they can trace its location and prevent future outbreaks.
Blockchain technology allows systems to react much faster in the event of a hazard. It also has many other uses in the modern world.
Blockchain technology is safe, even if it’s public. People can access the technology using an internet connection.
Have you ever been in a situation where you had all your data stored at one place and that one secure place got compromised? Wouldn't it be great if there was a way to prevent your data from leaking out even when the security of your storage systems is compromised?
Blockchain technology provides a way of avoiding this situation by using multiple computers at different locations to store information about transactions. If one computer experiences problems with a transaction, it will not affect the other nodes.
Instead, other nodes will use the correct information to cross-reference your incorrect node. This is called “Decentralization,” meaning all the information is stored in multiple places.
Blockchain guarantees your data's authenticity—not just its accuracy, but also its irreversibility. It can also be used to store data that are difficult to register, like legal contracts, state identifications, or a company's product inventory.
Blockchain has many advantages and disadvantages.
I’ll answer the most frequently asked questions about blockchain in this section.
Blockchain is not a cryptocurrency but a technology that makes cryptocurrencies possible. It's a digital ledger that records every transaction seamlessly.
Yes, blockchain can be theoretically hacked, but it is a complicated task to be achieved. A network of users constantly reviews it, which makes hacking the blockchain difficult.
Coinbase Global is currently the biggest blockchain company in the world. The company runs a commendable infrastructure, services, and technology for the digital currency economy.
Blockchain is a decentralized technology. It’s a chain of distributed ledgers connected with nodes. Each node can be any electronic device. Thus, one owns blockhain.
Bitcoin is a cryptocurrency, which is powered by Blockchain technology while Blockchain is a distributed ledger of cryptocurrency
Generally a database is a collection of data which can be stored and organized using a database management system. The people who have access to the database can view or edit the information stored there. The client-server network architecture is used to implement databases. whereas a blockchain is a growing list of records, called blocks, stored in a distributed system. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, timestamp and transaction information. Modification of data is not allowed due to the design of the blockchain. The technology allows decentralized control and eliminates risks of data modification by other parties.
Blockchain has a wide spectrum of applications and, over the next 5-10 years, we will likely see it being integrated into all sorts of industries. From finance to healthcare, blockchain could revolutionize the way we store and share data. Although there is some hesitation to adopt blockchain systems right now, that won't be the case in 2022-2023 (and even less so in 2026). Once people become more comfortable with the technology and understand how it can work for them, owners, CEOs and entrepreneurs alike will be quick to leverage blockchain technology for their own gain. Hope you like this article if you have any question let me know in the comments section
FOLLOW US ON TWITTER
RSS Rabbit links users to publicly available RSS entries.
Vet every link before clicking! The creators accept no responsibility for the contents of these entries.
Relevant
Fresh
Convenient
Agile
We're not prepared to take user feedback yet. Check back soon!